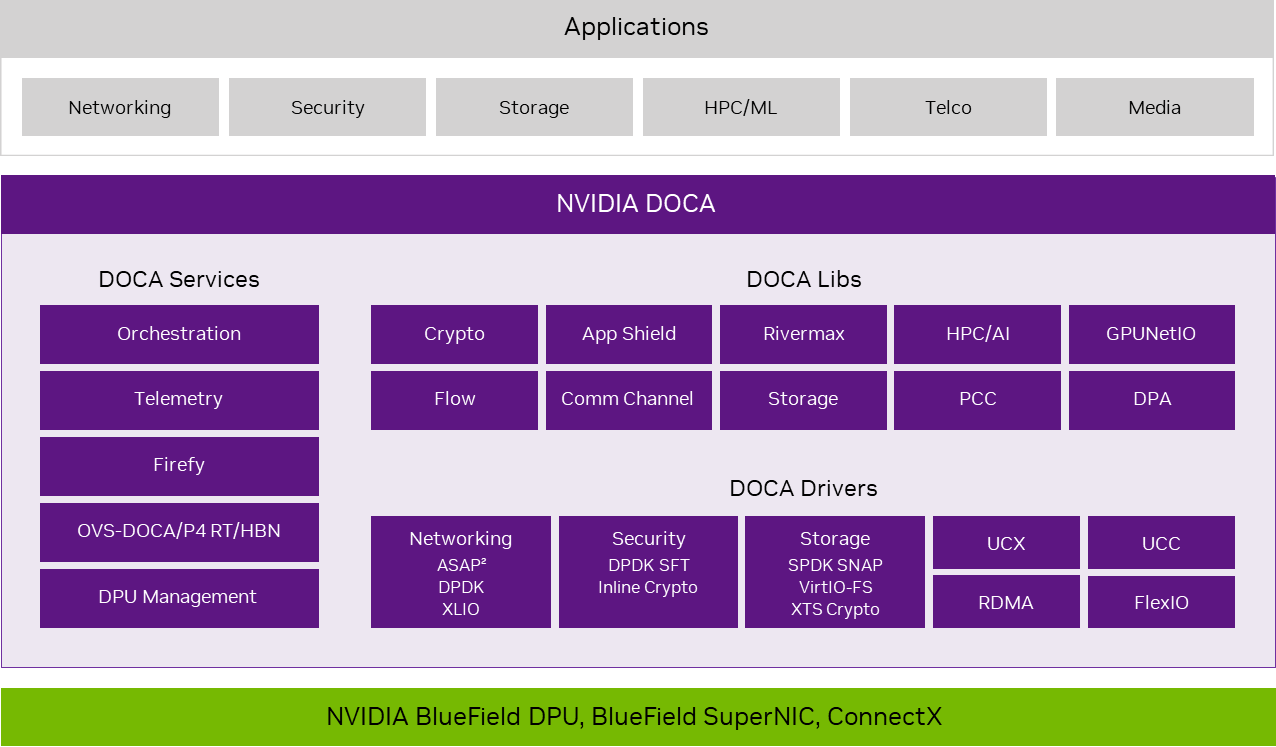
NVIDIA DOCA enhances the capabilities of NVIDIA networking platforms by providing a comprehensive software framework for developers to leverage hardware acceleration, boosting performance, security, and efficiency. Its ecosystem of APIs, libraries, and tools streamlines development for data center infrastructure, enabling workload offloading, acceleration, and isolation to support modern, efficient data centers.
Today, DOCA is used by many major CSPs and NVIDIA Cloud Partners (NCPs) and provides a standardized platform to rapidly develop and deploy innovative solutions. This approach accelerates time to market, reduces costs, and enables partners to focus on their core strengths while using NVIDIA hardware acceleration.
The open ecosystem fostered by DOCA promotes collaboration and interoperability, creating a diverse array of complementary solutions. Partners can explore emerging markets such as AI-driven networking, advanced security, and high-performance storage, positioning themselves at the forefront of data center innovation.
The latest release of DOCA 2.9 marks a major advancement in AI compute fabrics and cloud computing infrastructure. This extensive update introduces many new features and improvements to help transform the high-performance computing and networking landscape.
Optimizing AI networks with an enhanced east-west compute fabric
The highlights in the DOCA 2.9 release include improved congestion control and a new telemetry library essential for optimizing network traffic within the data center—providing better performance, efficiency, visibility, and control.
Spectrum-X 1.2 reference architecture support
The Spectrum-X (SPC-X) 1.2 reference architecture received several enhancements, targeting east-west Ethernet AI cloud environments. This update supports massive scale-out capabilities, accommodating up to 128,000 GPUs in a single fabric. The architecture uses the powerful combination of NVIDIA BlueField-3 SuperNICs and NVIDIA Spectrum-4 switches, connected to NVIDIA DGX H100 and NVIDIA HGX H100 platforms, to deliver unprecedented performance and efficiency for AI workloads.
DOCA 2.9 also improves telemetry capabilities and the congestion control algorithm for Spectrum-X. This allows for more granular, real-time monitoring of network performance, and improved topology detection, which is crucial for optimizing AI workloads at scale and distances.
DOCA congestion control
DOCA 2.9 advances the congestion control algorithm for high-performance computing and AI workloads, called NVIDIA Network Congestion Control (NVNCC).
The general availability of NVNCC Gen2 and InfiniBand Congestion Control IBCC marks a major milestone. IBCC is specifically optimized for AI workloads over InfiniBand, while NVNCC enhances the Spectrum-X congestion control algorithm with improved topology detection capabilities, now supporting long-distance RoCE.
DOCA telemetry library
New to this release, the DOCA telemetry library introduces high-frequency sampling capabilities, advancing network monitoring for AI-driven environments. This update enables counter readings at sub-100 microsecond intervals, a sizable leap from the previous 0.5-1-second frequency.
Key features include new APIs for specifying counters, intervals, and frequency, along with support for multiple performance counters such as RX/TX bytes, ports, congestion notifications, and PCIe latency. These enhancements cater to critical use cases like high-frequency telemetry (HFT) for cluster-wide anomaly detection and local performance analysis for application profiling.
North-south cloud computing infrastructure is enhancing connectivity and security
The north-south improvements in DOCA 2.9 focus on enhancing the connectivity between cloud resources and external networks.
DOCA Flow
DOCA 2.9 introduces an exciting new feature to DOCA Flow: the ‘tune’ performance analysis tool. Currently in the alpha stage, this tool is seamlessly integrated into the DOCA-Flow delivery package, offering users unprecedented insights into their network flow configurations.
The ‘tune’ tool provides a visual representation of configured pipelines, enabling users to gain a clear understanding of their flow structures. This visualization capability enables administrators and developers to quickly identify and optimize flow configurations.
OVS-DOCA
OVS-DOCA is generally available, bringing with it local mirroring capabilities, and adding a step forward in software-defined networking for NVIDIA BlueField DPUs. This long-term support (LTS) release offers users a stable, high-performance alternative to legacy OVS solutions, providing better efficiency and expanded features for modern networking environments, using DPDK or kernel datapath.
The GA release introduces key enhancements that elevate the capabilities of DOCA, including a major performance boost for the connection tracking (CT) feature through the DOCA Flow API. Users can expect a 100% improvement in connections per second (CPS) and up to a 50% increase in packets per second (PPS). Scalability and throughput have been enhanced with support for up to three NICs, for more flexible and powerful networking configurations.
DOCA host-based networking 2.4
DOCA host-based networking (HBN) continues to evolve and version 2.4 brings numerous enhancements to controller-less VPC networking for bare-metal-as-a-service environments. Building on the foundation of BGP EVPN, DOCA HBN 2.4 introduces impressive scalability improvements, supporting up to 8,000 VTEPs and 80,000 Type-5 routes.
The latest release enhances ECMP routing with kernel next-hop groups and OVS-DOCA failover, improving network resilience and performance. A key addition is the Stateful SNAT+PAT for overlay gateways, enabling private tenant IPs to access external networks through a shared public IP address.
DOCA FireFly
The enhanced DOCA Firefly service brings advanced time synchronization capabilities to NVIDIA DPUs through hardware acceleration. This update introduces two notable features: Synchronous Ethernet (SyncE) support and Data Transfer Service (DTS) integration.
SyncE provides high-precision frequency synchronization between network devices, crucial for telecommunications networks, particularly in mobile infrastructure. DTS support enables PTP information transmission over the telemetry channel, allowing for continuous network time service monitoring.
NVIDIA Rivermax SDK
The Rivermax SDK received enhancements focused on reducing latency, minimizing CPU usage, and maximizing bandwidth and GPU utilization for data-intensive applications. A key addition is support for Internet Protocol Media Experience (IPMX), the emerging open standard for AV over IP in professional audiovisual environments.
Underpinned by Rivermax, DOCA 2.9 also supports NVIDIA Holoscan for Media; a certified platform tailored for the media and entertainment industry. This feature optimizes the handling of uncompressed and compressed video streams, streamlining I/O operations for high-performance media processing.
NVIDIA DOCA App Shield
Enhancements to the DOCA App Shield library boost its capabilities in host monitoring and threat detection. A key addition is the inclusion of pre-generated OS profiles, streamlining the setup process for various operating systems.
For Linux environments, App Shield now offers advanced container monitoring features, enabling security teams to keep a vigilant eye on containerized workloads. The service has been expanded to list network connections and provide detailed information on network connections per process, offering deeper insights into potential security threats.
DOCA SNAP virtio-fs
The beta version of DOCA SNAP virtio-fs, is a service for secured and accelerated file system storage that leverages the power of NVIDIA BlueField-3 DPUs. This solution exposes local file system semantics to the host using the in-box virtio-fs driver, while running remote file system storage logic directly on the DPU.
The release also introduces a beta version of SNAP Virtio-fs, delivered as a public NGC service container. It’s enabled with the NFS Linux kernel file system, integrated into the BlueField-3 kernel. Developers can create custom file system stacks based on SPDK FSDEV, offering flexibility and performance optimization.
This solution enables cloud-scale distributed file system storage in AI compute servers, providing a secured environment with isolation and policy enforcement, while accelerating performance and offloading hypervisor tasks.
Open Virtual Network Bare-Metal Tenant Isolation
DOCA 2.9 includes a new orchestration service, enhancing tenant isolation in software-defined networking (SDN) environments. The Open Virtual Network (OVN) Bare-Metal tenant isolation feature secures north-south traffic in multi-tenant environments, ensuring AI workloads stay secure and separate, even in dense compute clusters.
Built on upstream OVN, this service provides streamlined, robust APIs for tenant isolation, along with an Ansible playbook for effortless deployment on BlueField DPUs. The key innovation lies in offloading and accelerating SDN-based tenant BlueField DPUs to improve both speed and efficiency by isolating specific processes. This central organization enables easy changes to isolation settings using API calls, providing more control over network management. This makes it perfect for AI clouds and factories that want to create multi-tenant clouds using SDN.
DOCA 2.9 streamlines and simplifies the device management process necessary for large-scale deployments. This release also provides developers with new optimization and analysis tools that offer improved insights into application and datapath performance.
DOCA Management Service (DMS)
DOCA Management Service (DMS) also moved to GA status, offering enhanced capabilities for managing BlueField DPUs and SuperNICs. This update introduces the ability to manage multiple devices through a single API endpoint, streamlining operations in complex, multi-device environments.
A key improvement is the support for configuration ‘persistency’ across node reboots, ensuring that device settings remain intact during system restarts. This is complemented by new bulk import/export features for device configurations, enabling efficient management of large-scale deployments.
DOCA data path accelerator
Enhancements for the data path accelerator (DPA) toolkit offer developers more powerful performance optimization and analysis tools. A standout feature is the integration of DPA performance counters with a new Nsight tool, providing deeper insights into application performance.
A major addition is the DOCA-DPA-Comms library, currently in beta. This library simplifies the implementation of DPA-based datapaths, offering a higher level of abstraction for developers. It’s available for both BlueField-3 DPUs and the upcoming NVIDIA ConnectX-8 SuperNIC, ensuring broad compatibility across the NVIDIA advanced networking hardware portfolio.
Platform and DOCA packages for streamlined deployment and support
Improving the user experience is central to the evolution of DOCA. This release includes many features intended to simplify and improve deployment, such as the DOCA-Host profile DOCA-ROCE, which caters to environments that require RDMA over Converged Ethernet capabilities.
NVIDIA also introduced PLDM firmware updates for BlueField-3. This beta release enables seamless firmware updates using standard PLDM over MCTP over PCIe, for servers to operate normally until activation. This zero-trust feature supports both NIC and DPU modes and eliminates the need for DPU-BMC 1GbE connectivity.
In addition, this release marks the final Long Term Support (LTS) standalone release of MLNX_OFED which is now available as the host profile ‘DOCA-OFED’.
Transitioning from the MLNX_OFED suite of drivers and tools for InfiniBand and Ethernet solutions to DOCA-OFED enables a unified, scalable, and programmable networking stack integrated within the DOCA framework. Learn more about the MLNX_OFED to DOCA-OFED transition.
Learn more
NVIDIA DOCA 2.9 marks significant advancements in both AI compute fabric and cloud computing infrastructure. Download NVIDIA DOCA to begin your development journey with all the benefits DOCA has to offer.